Summary:1. The role of the shunt
It is used to expand the measuring current range of the instrument, and it...
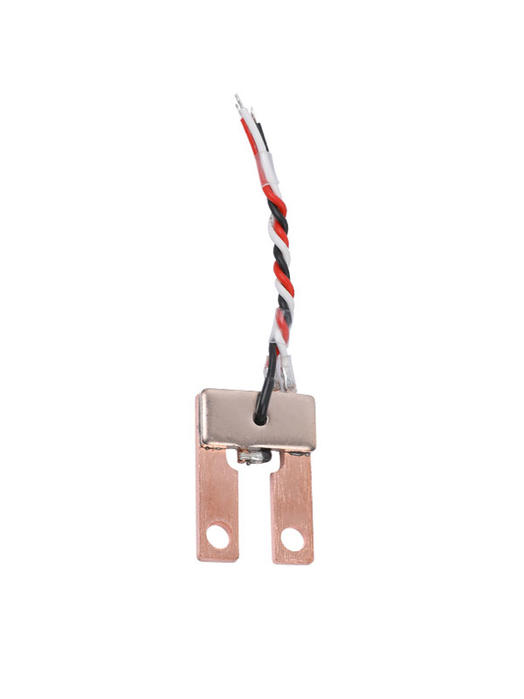
1. The role of the shunt
It is used to expand the measuring current range of the instrument, and it is used for current limiting and current sharing sampling detection in the loop of the instrument, communication system, electronic whole machine, and automatic control power supply. A shunt is based on the principle that a voltage is generated across a resistor when a DC current passes through it. There are fixed fixed value shunts and precision alloy resistors, and the detected voltage is used for instruments, control circuits, etc. The shunts have manganese-nickel-copper alloy resistance rods and copper strips, and are plated with nickel.
The shunt is used to measure DC current, and it is made according to the principle that a voltage is generated across the resistor when the DC current passes through the resistor. It is made of insulating ceramics and has evenly distributed small holes. After the shielding gas sprayed from the welding torch passes through the shunt, it is sprayed evenly in a laminar flow to improve the protection effect.
2. How the shunt works
The shunt is used to measure DC current and is made according to the principle that a voltage is generated across the resistor when the DC current passes through the resistor.
The splitter replicates, aggregates, and filters the input data to the network splitter, converts 10 Gigabit POS data into Gigabit LAN data through protocol conversion, and performs load balancing output according to a specific algorithm, while ensuring all data in the same session. packets, or all packets for the same IP user are output from the same interface.
The shunt is actually a resistor with a small resistance value. When a DC current passes through, a voltage drop is generated for the DC ammeter to display.